Here we can define, 2 events: A and B. If the occurrence of event A doesn’t affect the occurrence of event B, these events are called independent events. In this case the probability of P (A ꓵ B) = P (A) * P (B).
If are dependent events we can define:
- event A is the probability of the event we’re trying to calculate;
- event B is the condition that we know or the event that has happened.
We can write the conditional probability as
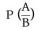
the probability of the occurrence of event A given that B has already happened.

The Bayes theorem describes the probability of an event based on the prior knowledge of the conditions that might be related to the event. If we know the conditional probability
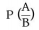
we can use the bayes rule to find out the reverse probabilities
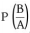
How can we do that?

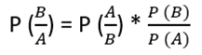
The Bayesian view of probability is related to degree of belief. It is a measure of the plausibility of an event given incomplete knowledge.