The mean of the sampling distribution of the mean is the mean of the population from which the scores were sampled. Therefore, if a population has a mean μ, then the mean of the sampling distribution of the mean is also μ. The symbol μM is used to refer to the mean of the sampling distribution of the mean. Therefore, the formula for the mean of the sampling distribution of the mean can be written as:
μM = μ
Variance
The variance of the sampling distribution of the mean is computed as follows:
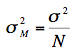
That is, the variance of the sampling distribution of the mean is the population variance divided by N, the sample size (the number of scores used to compute a mean). Thus, the larger the sample size, the smaller the variance of the sampling distribution of the mean.
(optional) This expression can be derived very easily from the variance sum law. Let’s begin by computing the variance of the sampling distribution of the sum of three numbers sampled from a population with variance σ2. The variance of the sum would be σ2 + σ2 + σ2. For N numbers, the variance would be Nσ2. Since the mean is 1/N times the sum, the variance of the sampling distribution of the mean would be 1/N2 times the variance of the sum, which equals σ2/N.
The standard error of the mean is the standard deviation of the sampling distribution of the mean. It is therefore the square root of the variance of the sampling distribution of the mean and can be written as:
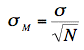
The standard error is represented by a σ because it is a standard deviation. The subscript (M) indicates that the standard error in question is the standard error of the mean.