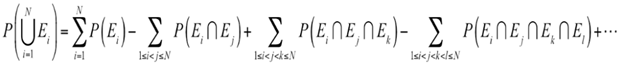Boole inequality and calculation of union probability of n arbitrary events:
In probability theory, Boole’s inequality, also known as the union bound, says that for any finite or countable set of events, the probability that at least one of the events happens is no greater than the sum of the probabilities of the individual events.
Formally, for a countable set of events A1, A2, A3, …, we have
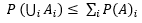
For n=2 events: P(A⋃B) = P(A)+P(B)-P(A⋂B), for arbitrary event, it is P(A⋂B) >0, which is subtracted, and so it follows that P(A⋃B) P(A)+P(B).
For n=3 events: P (A⋃B⋃C) P(A)+P(B)+P(C)-P(A⋂B)- P(A⋂C)- P(B⋂C)+ P(A⋂B⋂C).
Fon n events: